Go Home
Go To Introduction
This is Book 1
Chapter 1 - Electricity
Chapter 1.2 - The Numbers
Chapter 2 - Sharing and Bonding
Chapter 3 - Voltage
Chapter 3.2 - Voltage Static
Chapter 3.3 - Batteries
Chapter 3.4 - Solar - Others
Chapter 4 - Resistance
Chapter 4.2 - Parallel Resistance
Chapter 4.3 - Voltage Dividers
Chapter 5 - Semiconductor
Chapter 5.2 - PNP NPN Junctions
Chapter 6 - Capacitor
Back To The Guide
To Book 2
The Battery - Chemical Properties
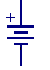
This is the schematic symbol for a battery. Take a moment and follow
this link to check out The Battery
For many years the low cost acidic battery of choice for radios and electronics
has been the zinc carbon battery. In recent years it has loosing ground to its
competition, the alkaline battery, and the lithium-ion battery or Li-ion battery.
Battery Types
Common commercial Dry-Cell batteries on the market today
Zinc-Carbon Cell - Voltage 1.5 volts
When using the zinc-carbon battery, over the life of the cell the voltage level
will start to drop off until is expires. This causes a flashlight, for example,
to not be very bright after it has been used for a while. The Zinc-Carbon cell
is not re-chargeable. This means the chemical reaction can not be reversed
within the cell by using a charger.
The construction of the zinc-carbon cell uses an zinc outer shell material in
the shape of a storage can, and is called the anode of the battery. Recall
that the anode is the negatively charge (-) side of the cell. The center post,
the cathode, is a type of carbon called graphite. The cathode represents the
positively side (+) of the cell. The electrolyte is an acidic type of paste
which is a combination of ammonium chloride (NH4Cl) and manganese dioxide (MnO2)
Chemically an oxidation reduction reaction takes place.
Half Reaction
2 NH4 + 2 MnO2 + 2e- - - - > Mn2O3 + 2 NH3 + H2O
Half Reaction
Zn (s) - - - > Zn2+ + 2e-
Full Reaction
Zn + 2 NH4Cl + 2 MnO2 - - - > ZnCl + Mn2O3 + 2 NH3 + H2O + 2e-
What this means in unscientific terms is that the battery has potential
energy (2e-). It is waiting to give up this energy in trade for a chemical
reaction. So when the user uses electricity, a chemical reaction takes place,
moving electrons (2e-) from one plate, through the circuit and ending up
with the 2e- on the other plate. That is the flow of electricity. The battery
can do this until it has depleted its ability to produce this chemical
reaction. This battery is then considered dead, and needs to be properly
recycled.
These cells that use a zinc casing generally have a short life span due the
zinc can become porous and the zinc is converted to zinc chloride. The
substances within the battery are very corrosive to metals. If (and when)
the substances in this type of cell start to leak out, the electrolyte can
damage or destroy electronic equipment.
Click the type ==> Alkaline Dry Cell - Voltage 1.5 volts
Click the type ==> Nickel-Cadmium Cell - Voltage 1.2 volts
Click the type ==> Silver-Oxide Cell: Voltage 1.6 volts
The Generator - Electromagnetic Properties
One process of creating electricity is by generating electromagnetic electricity.
In its simplest form, this is when a wire (or wire segment) and a magnetic field
pass by one another. Generally the magnetic field is stationary and the wire
portion of the generator moves, but this is not always the case. Many small
gasoline engines have the magnet attached to the flywheel and a coil of wire is stationary.
Regardless of which part moves and which is stationary, this action is described
as having a wire segment cutting the magnetic field.
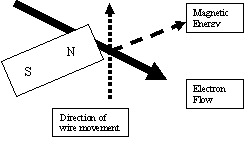
To expand this process in more detail we will introduce the Left Hand Rule. Using ones
left hand, place the hand out with the thumb pointing up (y axis) and index finger
pointing straight out (x axis) at a right angle with the thumb. Now open the middle
finger (z axis) to be at right angles with the index finger.
The index finger represents the direction of the magnetic energy coming out of the
north pole of the magnet. The thumb indicates the direction, the conductor (wire)
is moving along the face of the magnetic field. The middle finger represents both
the conductor and points in the direction the electrons are flowing along the
conductor.
A single wire crossing a magnetic field produces such a small amount of electricity
that it would be hard to measure or use in our daily activities.
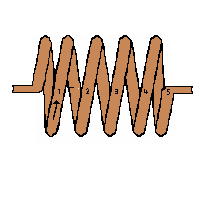
If we had a conductor with 5 loops of wire in a coil the result would produce 5
times more voltage than is produced in the single loop example. A 300-loop coil
would produce about 300 times the voltage.
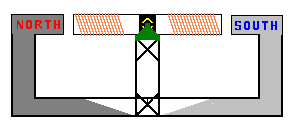
Now, if we were to put coils of wire on a shaft and mounted the shaft so it
could continuously rotate inside a magnetic field we will continuously get
electricity. This is exactly what happens inside a generator.
Many coils of wire are wrapped around an armature
(center metal component) of the generator. The north and south poles are part of
the stationary or stator section of the generator.
« Previous Chapter Next Chapter »
Email us: info@shoeboxkits.com