Chapter 4.3
Voltage Divider
Introduction
Chapter 1 - Electricity
Chapter 1.2 - The Numbers
Chapter 2 – Sharing and Bonding
Chapter 3 - Voltage
Chapter 3.2 – Voltage Static
Chapter 3.3 - Batteries
Chapter 3.4 – Solar - Others
Chapter 4 - Resistance
Chapter 4.2 – Parallel Resistance
Chapter 4.3 – Voltage Dividers
Chapter 5 - Semiconductor
Chapter 5.2 - PNP NPN Junctions
Chapter 6 – AC and Hertz
Chapter 7 - Magnetism
Chapter 7.2 - Inductors
Chapter 8 - Capacitor
Chapter 9 - IC's and Amplifier
Chapter 10 - 555 Timer
Chapter 11 - Logic
Chapter 12 - Power Supply
|
|
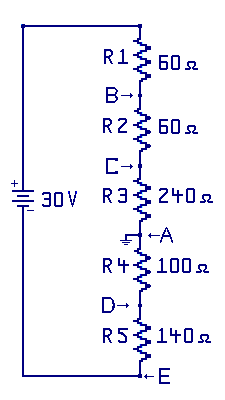 A voltage divider can be a simple series circuit that divides up the supply
voltage (potential) into one or more lower levels of voltage (potential).
A voltage divider can be a simple series circuit that divides up the supply
voltage (potential) into one or more lower levels of voltage (potential).